Red Light Therapy Guide: Science, Skin Results & Proven Health Benefits
Share
In recent years, red light therapy (RLT) has gained attention for its ability to improve skin health, speed wound healing, ease pain, and even support hair growth.But what exactly is RLT, and how does it work? Let’s dive into the science and see whether it lives up to the hype.
What Is Red Light Therapy (Photobiomodulation)?
Red light therapy, also known as photobiomodulation (PBM), uses safe, low levels of red or near-infrared light to stimulate the body’s cells. Its origins trace back to NASA in the 1990s, where it was studied to help astronauts heal wounds in space. Researchers discovered that specific wavelengths could boost cell growth, paving the way for today’s wellness and skincare applications.

At the cellular level, red and near-infrared light are absorbed by cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme critical for energy production. This process increases ATP (cell energy) while reducing oxidative stress, helping cells repair and function more effectively.
How Red Light Therapy Works at the Cellular Level
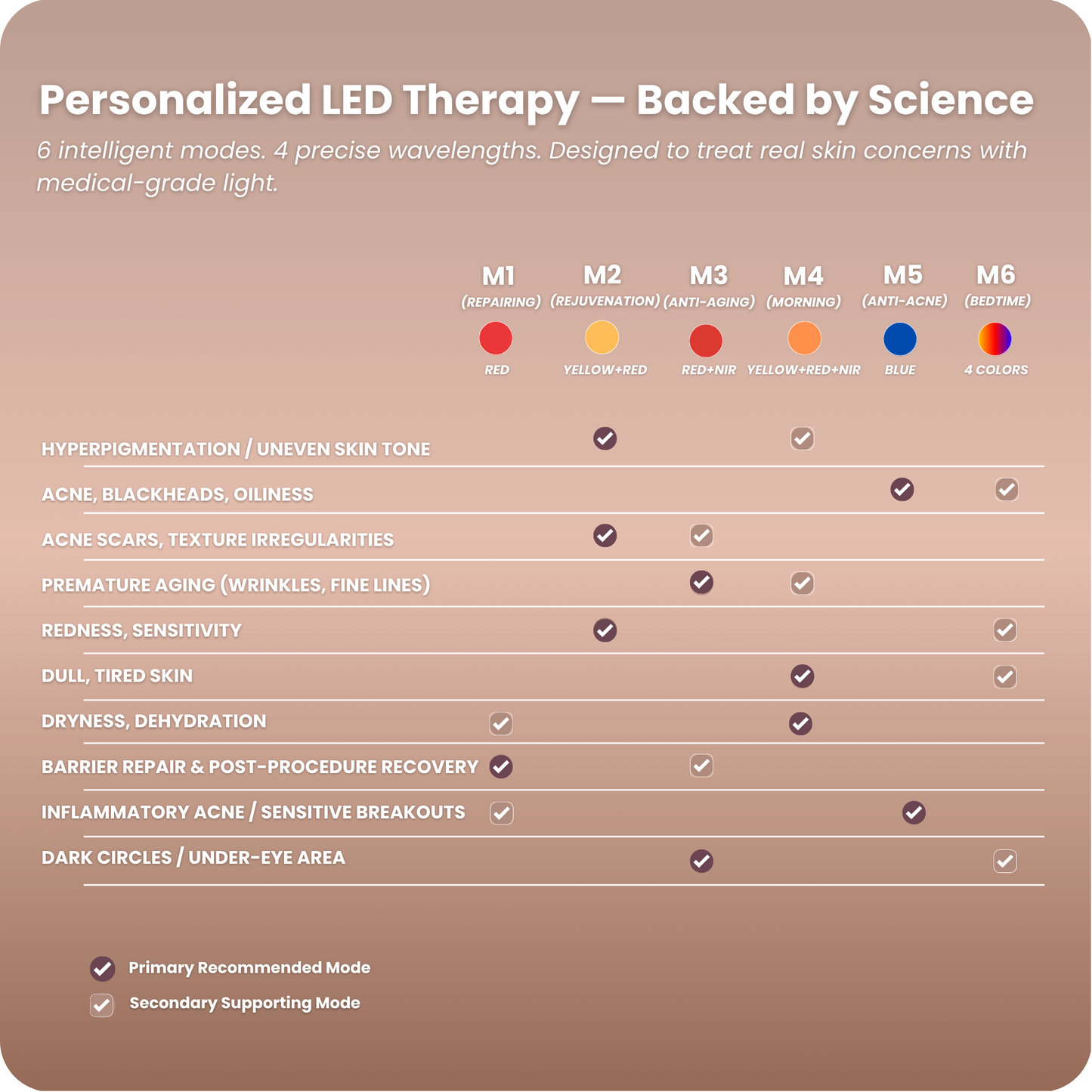
Different wavelengths penetrate the skin at different depths, each with unique effects:
- Red light (660nm): Stimulates collagen, reduces inflammation, and supports anti-aging.
- Blue light (415nm): Targets acne-causing bacteria, helping calm breakouts.
- Yellow light (590nm): Reduces redness and supports overall skin rejuvenation.
- Near-infrared (850nm): Penetrates deepest to encourage repair, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation.

Conditions Red Light Therapy May Help Improve
Studies suggest RLT may help with a variety of concerns, such as:
- Skin health: Wrinkles, acne, rosacea, eczema, psoriasis, and sun damage.
- Wound healing: Supporting recovery of burns, cuts, and ulcers.
- Hair growth: Stimulating follicles in cases of pattern hair loss.
- Pain relief: Reducing inflammation in arthritis, tendinitis, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
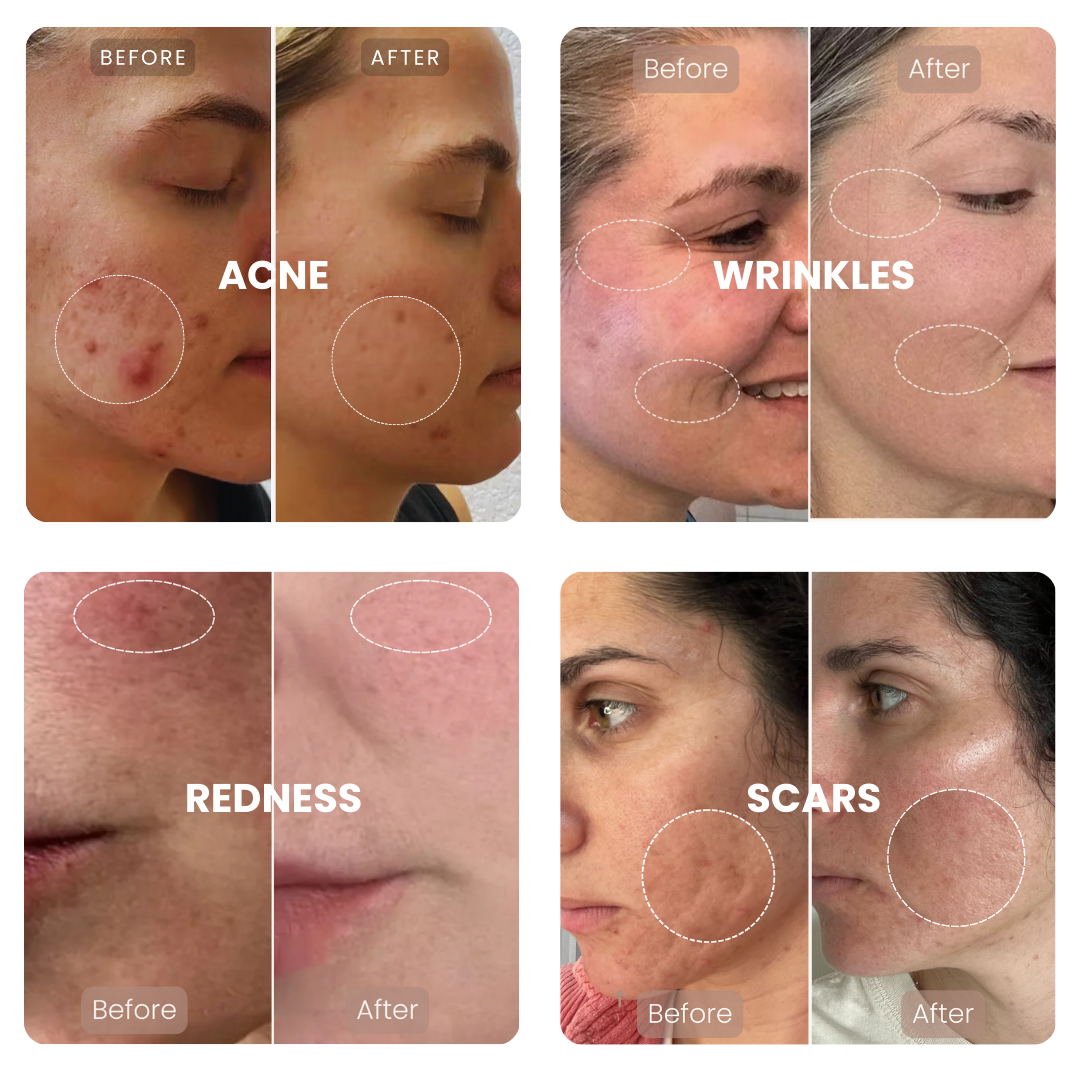
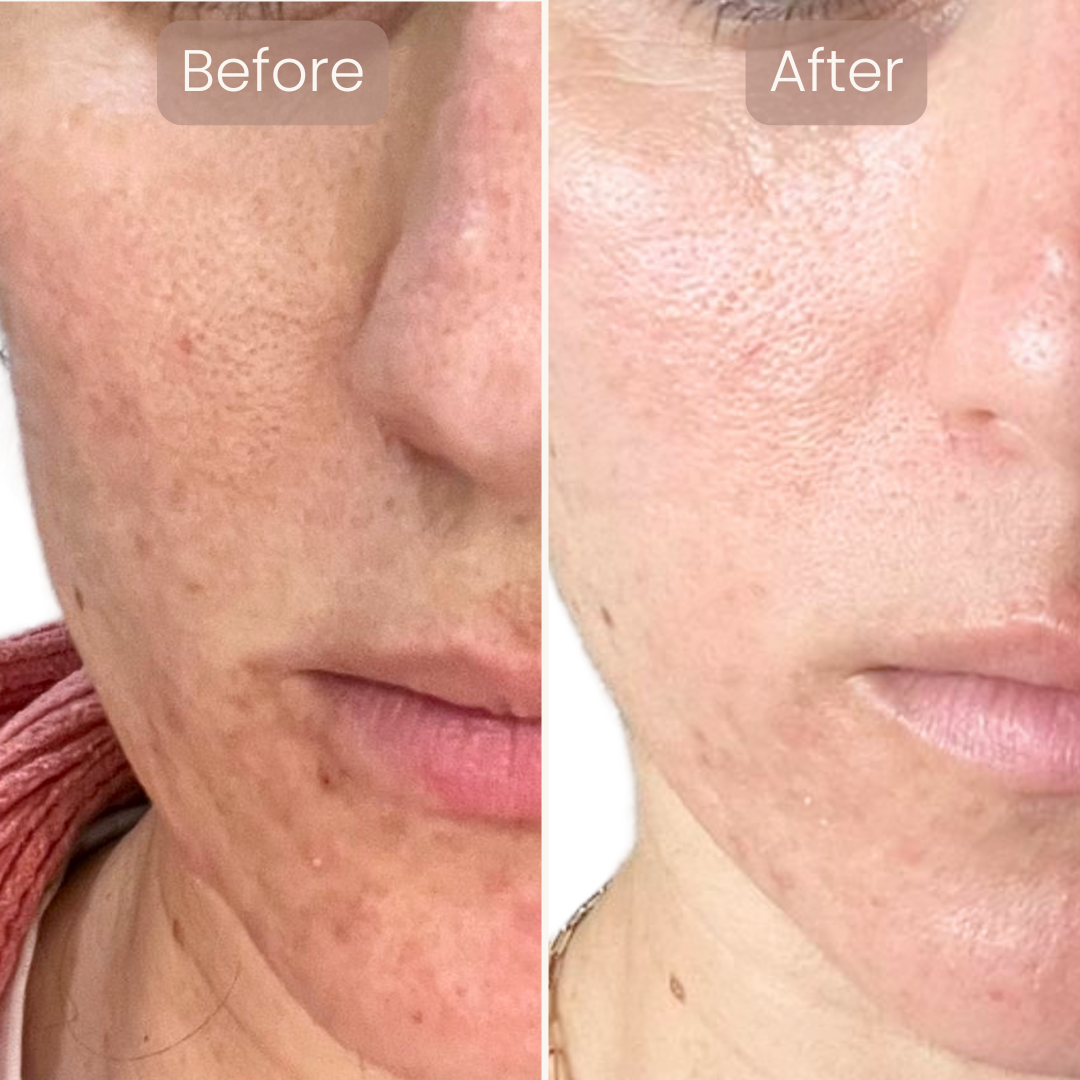
Research supports these outcomes. For example, a clinical study in the National Library of Medicine found that red and near-infrared light significantly improved skin elasticity and collagen density.
Is Red Light Therapy Safe?
Yes. Unlike ultraviolet (UV) light, red light therapy does not damage DNA or increase cancer risk. Most people tolerate it well with no side effects. However, if you have very sensitive skin or take photosensitizing medications, consult your doctor before starting.
Science-Backed Benefits of Red Light Therapy
- Boosts collagen and improves skin elasticity
- Reduces wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots
- Speeds up wound and burn recovery
- Helps clear acne, rosacea, and sun damage
- Alleviates pain and inflammation
- Stimulates hair regrowth in thinning areas
- Safe, non-invasive, and backed by clinical research

Final Thoughts
Red light therapy is a safe, non-invasive option with growing evidence for skin rejuvenation, wound healing, pain management, and hair regrowth. While more research will refine its long-term use, many people already experience meaningful benefits from consistent treatment.
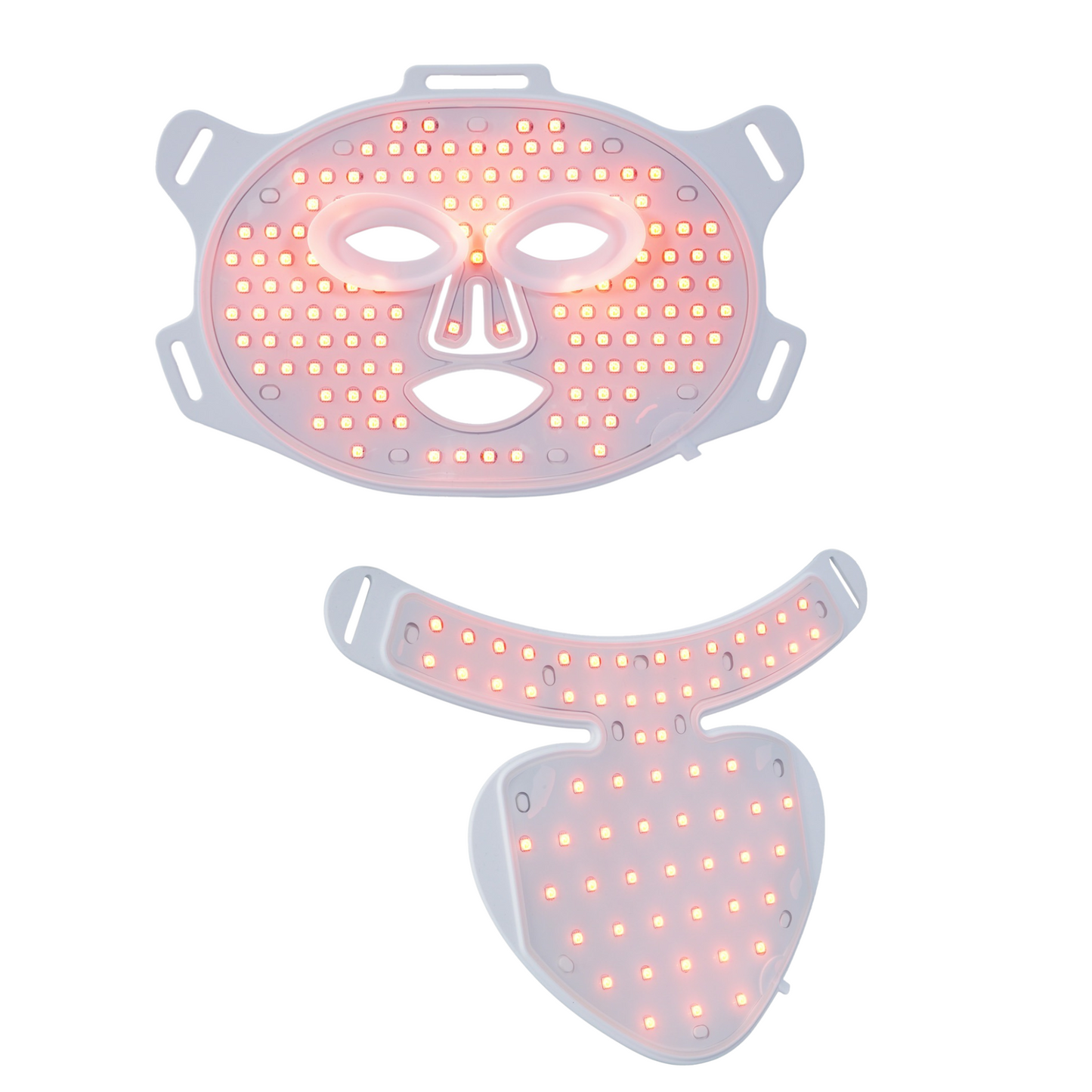
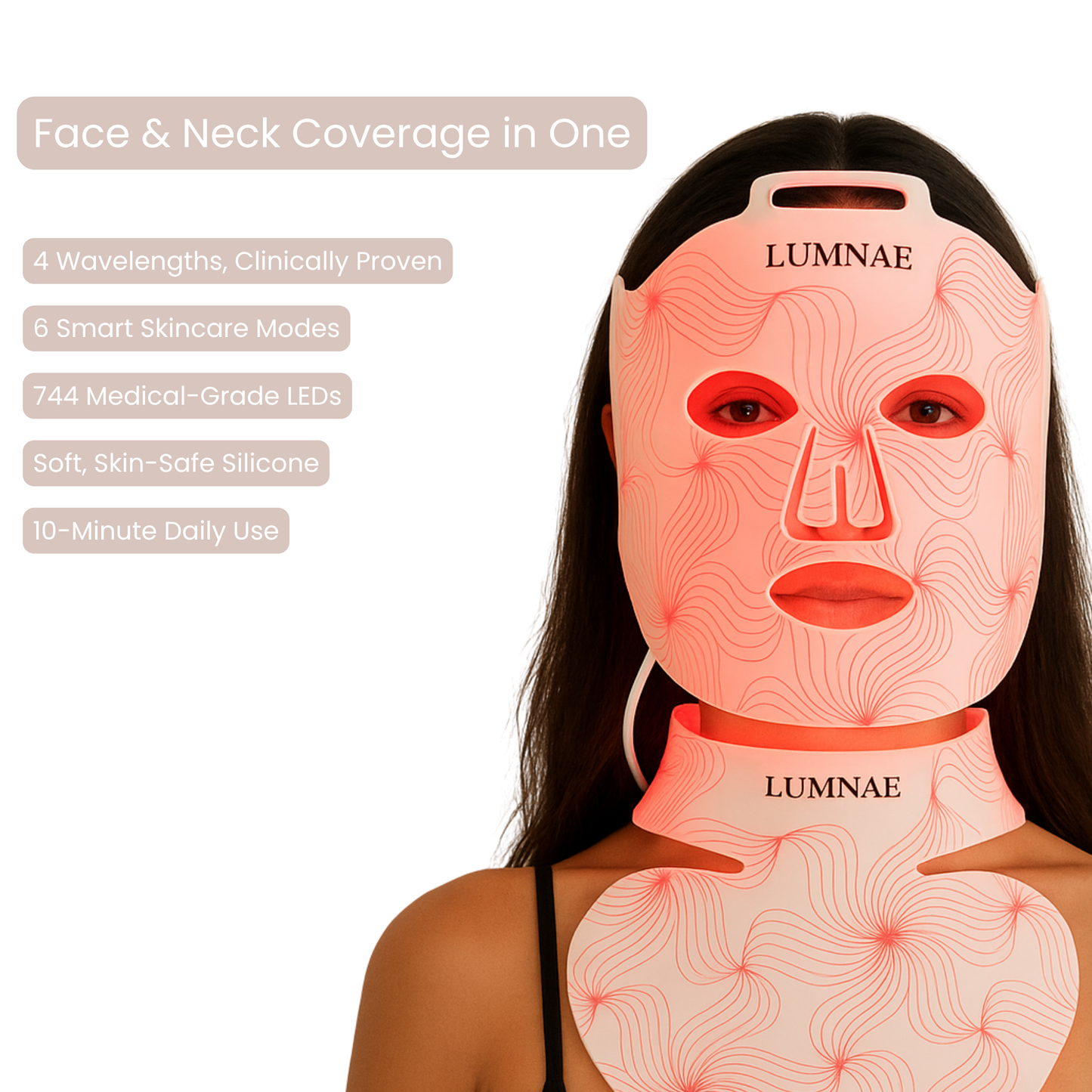
If you’d like to try RLT at home, the Lumnae™ LED Light Therapy Mask brings professional-grade wavelengths into your routine in just 10 minutes a day.
FAQs About Red Light Therapy
How often should I use red light therapy?
3–5 sessions per week are typically recommended. Visible improvements often appear after 4–6 weeks of consistent use.
Does red light therapy work for hair loss?
Yes. Red and near-infrared wavelengths can stimulate dormant follicles and improve hair density over time. Most users see results after 3–6 months of consistent use.
Can I use red light therapy with other skincare products?
Yes, but apply products after your session. Using skincare during treatment can block light penetration and reduce effectiveness.